GDP Center Publishes New Data on China’s Energy Financing

On February 23, 2021, the Global Development Policy (GDP) Center, an affiliated regional center at the Frederick S. Pardee School of Global Studies at Boston University, updated its interactive data project, The China’s Global Energy Finance Database, that exhibits financing for global energy projects by China’s two global policy banks – the China Development Bank (CDB) and the Export-Import Bank of China (CHEXIM) – in 2020.
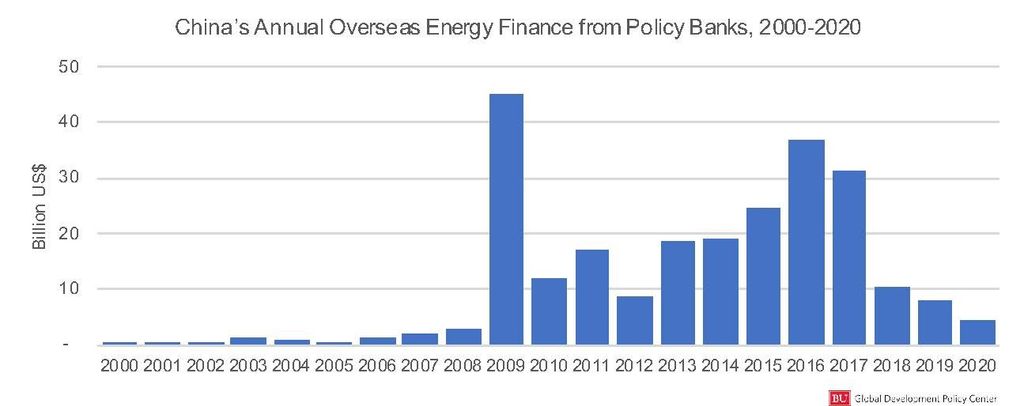
The new data set provides insights into the state of China’s global energy financing in 2020, the impact of debt relief efforts, which countries and sectors received financing, as well as what these developments mean for global climate and sustainability goals moving forward. The database recorded $4.6 billion of overseas energy sector finance in 2020; this is the lowest level since 2008 and represents a decrease of 43% from the $8.1 billion in lending to foreign countries recorded in 2019, as shown in the graphic below.
For more detailed insights, explore the China’s Global Energy Finance Database. Published alongside the database were a detailed policy brief and blog, which provide more information on the updated findings; the 2020 data release was also the subject of an article in Bloomberg.
The GDP Center is a university-wide research center affiliated with the Pardee School of Global Studies. The GDP Center’s mission is to advance policy-oriented research for financial stability, human well-being, and environmental sustainability. Visit the GDP Center’s website for more.